Source: Maryland Department of Agriculture Office of Resource Conservation
Mud can be a big problem wherever animals congregate, especially around gates, watering troughs, barn entrances, and feeding pads. If mud in these areas is making you and your horses miserable, follow these tips.
Manage Water Carefully
Manage water within your pasture to control potential nutrient losses. This may require diverting surface and roof runoff water away from pastures or paddocks. Always work to conserve water. Use a bucket of water rather than a hose to wash horses.
Plant Vegetative Cover
Planting a vegetative cover around buildings or on steep slopes can help minimize erosion and absorb nutrients while improving the appearance of your property. Commonly used covers include native grasses, shrubs, and groundcovers. It is important to reseed areas around watering troughs to maintain vegetative cover.
Install A Heavy Use Pad
Operations with 8,000 lbs. or more of live animal weight may qualify for cost-share assistance to install a concrete pad and other artificial surfaces to stabilize areas that are disturbed because of frequent and intensive use by livestock. Contact your soil conservation district to see if you qualify.
Smaller operations can install a heavy use pad by following the instructions outlined.
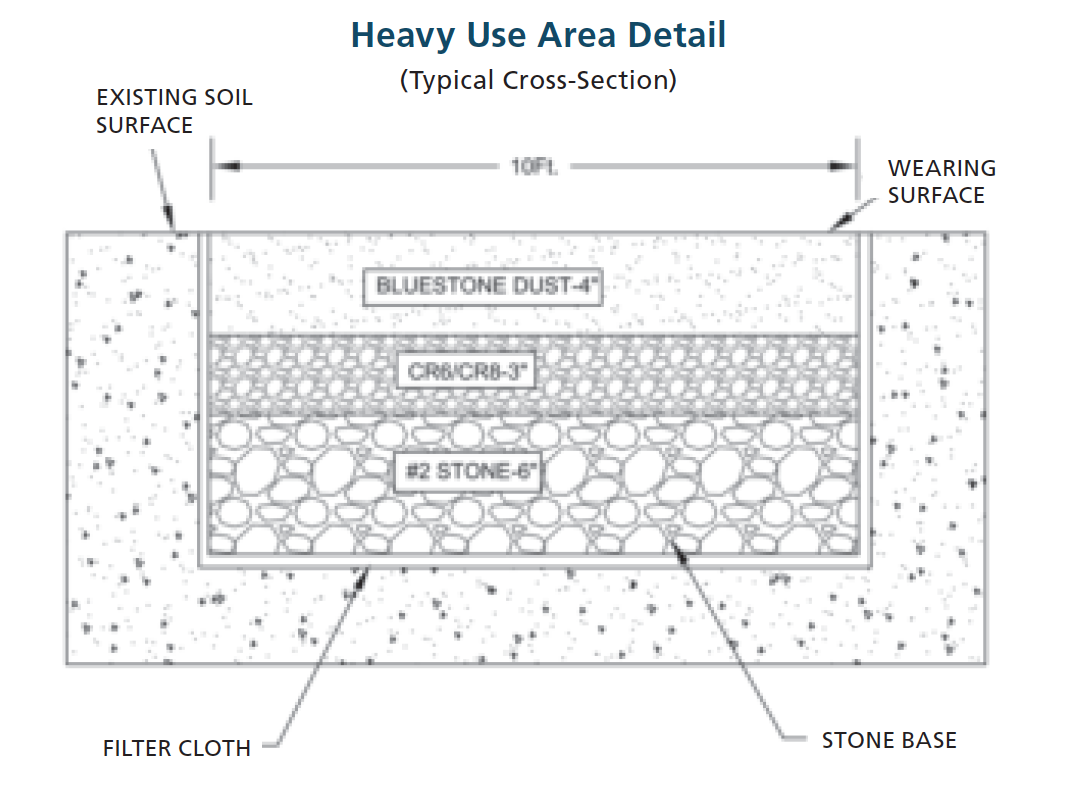
Do It Yourself: How to Install a Heavy Use Pad
Stone and geotextile fabric are the main components of a heavy use
pad. They allow water to slowly drain away without mixing with the soil. This heavy use pad is easy to install if you have a front loading tractor and can do simple excavation work. If not, you may need to hire someone with the necessary equipment.
Don’t skimp on the size of the pad. If you’re installing a pad around a trough, make it at least the length of one horse on each accessible side of the trough. Install gutters and downspouts on all buildings to divert water away from the heavy use pad. Downspout extenders, gravel trenches, and low berms are easy ways to reroute water. Contact your local soil conservation district listed on the back of this booklet for free advice on safely rerouting runoff.
• Excavate the area to a depth of 8 to 12 inches.
• Level the site.
• Install class SE non-woven filter fabric. If the fabric isn’t wide enough, refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for overlap.
• Add 6 inches of #2 stone (2 ½ inches in size).
• Compact stone with a roller or drive over the pad with a tractor.
• Install 3 inches of CR6 or CR8 stone. (CR6 ranges in size from dust to 3/4 inch wide. CR8 is smaller.)
• Top with 4 inches of bluestone dust or wood chips.
• Compact and level stone.
• Inspect regularly and repair as needed.
Give Mud the Boot to Reduce…
• Hoof health issues
• Bacterial and fungal leg infections
• Fly breeding areas
Prevent Water-borne Diseases
West Nile Virus is transmitted to humans and horses by mosquitoes. Minimize standing water around your property to eliminate mosquito breeding areas.
• Correct drainage problems in fields and empty standing water in containers.
• Just one-half inch of water in a discarded can or container will support dozens of mosquitoes.
• West Nile Virus vaccinations are available for horses.
• If you suspect that your horse has been infected, contact your veterinarian.
For more information on creating healthy farms, see MDA’s “A Horse Owner’s Guide to: Greener Pastures, Cleaner Streams, Healthier Horses“