Diagnostic imaging techniques for determining lameness in horses is constantly evolving and improving, assisting veterinarians to provide accurate diagnosis, prognosis and appropriate treatment options. Understanding imaging options will allow you to understand why your veterinarian has suggested one over another.
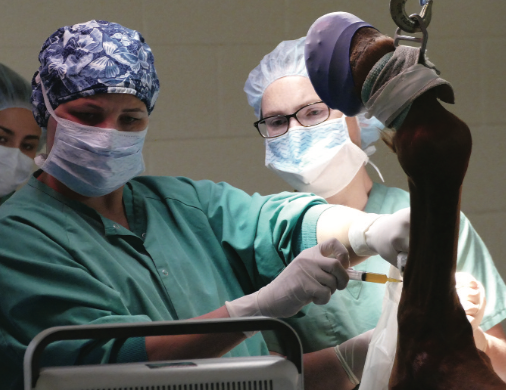
Ultrasonography is used to guide treatment of a hind proximal suspensory ligament lesion.
- Digital radiography(X-ray) provides clear, detailed images of bony structures of the horse and is used to diagnose fractures, bone cysts, and arthritis. However, radiographs create a two-dimensional image of three-dimensional bones, and thus can miss subtle abnormalities, especially in complex joints.
- Ultrasonography sends sound waves by a hand-held probe into the horse’s body. Structures with different densities reflect sound waves back to the probe, which in turn creates digital images. These high quality images are useful to monitor and diagnose soft tissue, joint and bone injuries; however, this technique cannot penetrate through bone, and only the surface of bone is visible.
- Nuclear Scintigraphy (Bone Scan) involves injecting the horse with radioisotope that tracks to actively changing bone and highlights bony injuries or changes. Using a gamma camera to scan the body, injured bone and tissue absorbs more radioisotope than healthy bone and tissue. This technique is useful for multiple limb lameness, inconsistent lame- ness, lameness detected at speed, kissing spine, neck arthritis and sacroiliac joints. But, it is a screening tool that often identifies a region to further investigate with additional imaging techniques to determine a specific diagnosis.
- ComputedTomography(CT) provides three-dimensional radiographs in real time, which can be manipulated to view at any angle. Contrast can be injected to image soft tissue damage. CT is particularly useful for dense bone, complex joints, detection of hairline fractures and for pre-operative planning for complex fractures.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is useful for bone, tendon, ligament and joint pain diagnosis. It is imperative to know the location of pain before imaging. The advantage of MRI is that it shows the chemistry of the tissue, rather than the mineral composition (radiographs and CT), or the sound characteristics (ultrasonography). Specifically, MRI can show where there is increased fluid within a tissue, which is a hallmark of inflammation and pain.
In collaboration with your primary care veterinarian, advanced imaging is carefully chosen for each specific injury. You can be sure that technology and expert evaluation by specialists will play a pivotal part in the ultimate treatment and recovery of your horse from injury.
 –Jennifer G. Barrett, DVM, PhD,
–Jennifer G. Barrett, DVM, PhD,
Diplomate ACVS, Diplomate ACVSMR Theodora Ayer Randolph Professor of Equine Surgery
For more information about diagnostic imaging and specialists at the EMC go to:
https://emc.vetmed.vt.edu/clinical-services/ diagnostic-imaging.html
or contact Kathy Ashland at (703) 771-6875
(sponsored content; originally appeared in the August 2018 issue of The Equiery)
The Marion duPont Scott Equine Medical Center (EMC) is a premier, full-service equine health facility conveniently located at Morven Park in Leesburg, Virginia. As an integral part of the Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine and Virginia Tech, the EMC offers an array of cutting-edge diagnostic and therapeutic technologies and veterinary expertise to provide innovative and cost-effective care for your horse. The EMC offers a broad range of general and advanced specialty services by appointment as well as comprehensive 24/7 emergency services. State of the art technology with cutting-edge expertise…
Serving you, your vet and your horse. Ask your vet about us, or visit us yourself!
703-771-6800 • www.vetmed.vt.edu/emc/
You’re Invited: Sign up (name and email address to emcinfo@vt.edu) for EMC’s free equine health alerts and notice of Tuesday Talks, a free, educational seminar series on topics of interest to the horse community. Like us on Facebook to stay informed about the latest advances in equine medicine and health.












